The GDP (Gross Domestic Product) of Japan has shrunk by 0.4% during the fourth quarter of 2023 compared to the year before. This was not expected, as many economists predicted a growth of 1%. This comes after growth rates went down by 3.3% in the third quarter, one of the largest contractions in a while. Two quarters in a row of a shrinking GDP are typically considered an economic recession.
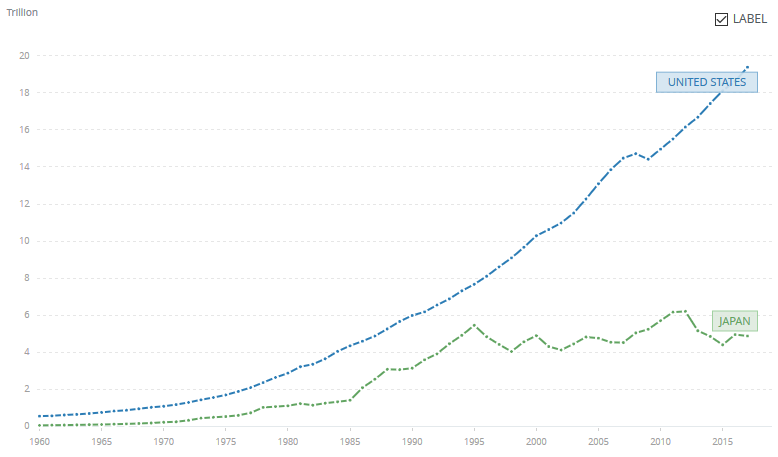
Japan’s economy faltered in the 1990s, due to an asset bubble that had been building up since the ’80s. This pushed Japan into a period of stagnation and deflation, known as the Lost Decade, now plural.
Figures from the Japanese Cabinet Office also show that Japan has been overtaken by Germany in GDP. As of 2023, Japan’s GDP was $4.2 trillion compared to Germany’s $4.4 trillion, according to economist Neil Newman. This was most likely due to the Japanese yen decreasing in value, and Newman states that if the yen recovers, Japan could potentially regain its position as one of the 3 largest economies.
However, the weakness of the yen has helped boost the share prices of many big companies as it makes Japanese exports cheaper overseas. This week, Tokyo’s Nikkei 225, the city’s main stock index, crossed $38,000 for the first time since 1990. This is because 1990 saw a collapse in Japanese property prices which caused an economic crisis. The Nikkei 225 had its record high stock price in 1989, priced at 38,915.87.